Under normal conditions synovial fluid has low viscosity which allows for easy movement of the joint. Non-Newtonian fluid a fluid in which viscosity does depend on shear rate eg.

Knee Effusions Arthrocentesis Interpretation Inflammatory Grepmed

Synovial Fluid Viscosity Test Is Promising For The Diagnosis Of Periprosthetic Joint Infection The Journal Of Arthroplasty
1
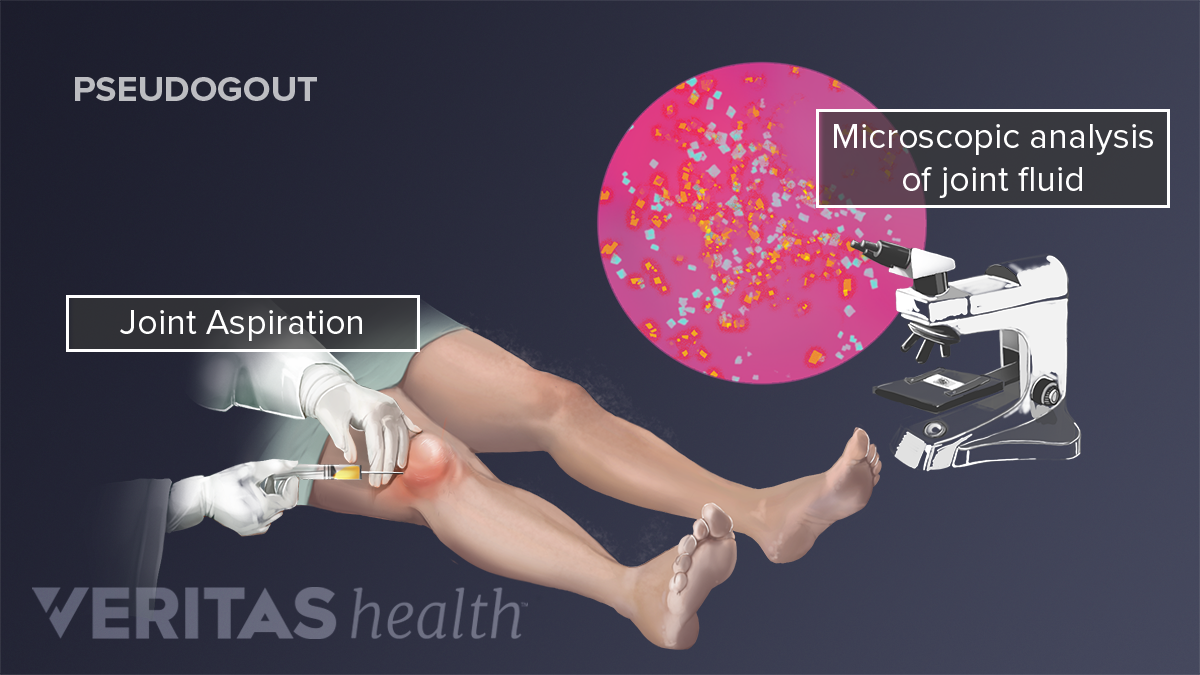
A number of tests can be conducted on synovial fluid after it is extracted from the joint space during a procedure called arthrocentesis.

Synovial fluid viscosity. In the people with osteoarthritis when the cartilage begins to break down and makes its way into the synovial fluid it leads to. Clinical Examination A comprehensive collection of clinical examination OSCE guides that include step-by-step images of key steps video demonstrations and PDF mark schemes. The dynamic viscosityη of a fluid is a measure of the resistance it offers to relative shearing motion.
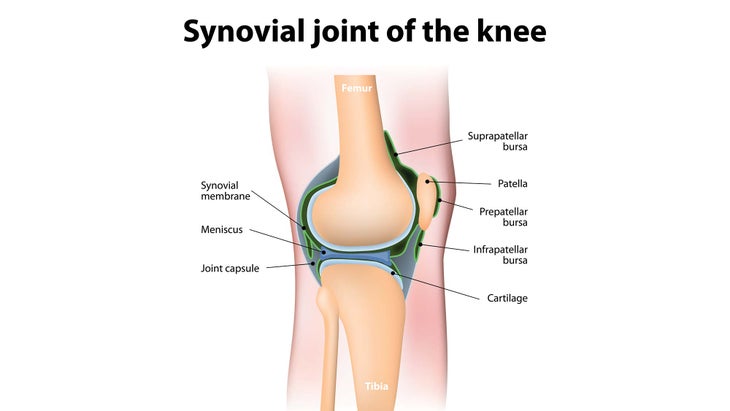
The synovial membrane is composed of adipose and fibrous tissue they have a smooth non-adherent surface that allows easy movement between tissues. Healthy joints contains high amounts of high molar mass hyaluronic acid HA molecules in the synovial fluid giving it the required viscosity for its function as lubricant solution which naturally cushion joints and other tissues. The synovial fluid present in diarthrotic joints will become thick the moment shear in order to protect the joint and subsequently.
Plasma viscosity is a specialised test that is usually only available in larger specialist laboratories. Synovial fluid is produced by the synovium and is composed of water inorganic salts and macromolecules hyaluronic acid lubricin and aggrecans which contribute to the boundary lubrication. Synovial fluid has a more vicious capacity when the pressure is applied.
η F Auh η τ uh. Furthermore CS inhibits the enzymes leukocyte elastase and hyaluronidase which are found in high concentration in the synovial fluid of patients with rheumatic diseases. Medical Laboratory Science Review Page 359.
A dilatant d aɪ ˈ l eɪ t ə n t d ɪ- also termed shear thickening material is one in which viscosity increases with the rate of shear strainSuch a shear thickening fluid also known by the initialism STF is an example of a non-Newtonian fluidThis behaviour is usually not observed in pure materials but can occur in suspensions. Viscosity increases and the fluid thickens over a period of continued stress. If your doctor thinks that you might have a condition that causes inflammation they may use this test to help diagnose and follow the course of this condition especially temporal arteritis or polymyalgia rheumaticaProduction of paraproteins is associated with some.
Lack of slipperiness is called as viscosity. Which of the following characteristic is higher for synovial fluid than for the serous fluid. The viscosity of synovial fluid is attributable to HA and serves as a lubricant for joint movements resulting in a coefficient of friction of nearly zero in joint cartilage.
Normal viscosity of the synovial fluid instantaneously resumes its lubricating function between shocks. This can be resolved by preparing either a dilution with saline or adding hyaluronidase to the specimen 400 units to 1 mL synovial fluid then incubate for 10 minutes at 37 C 1. Synovial fluid lubricates joints for smooth movement.
The total protein of synovial fluid is usually lower than serous fluids the upper reference limit being 20 gdL. This substance contributes to the viscosity and consistency of synovial fluid. If the viscosity is very high this can lead to difficulties when determining cell counts.
None of the above. Synovial fluid has rheopexy characteristics. VISCOSITY Viscosity is a quantitative measure of a fluids resistance to flow.
It is defined as the internal friction of fluid. Non-newtonian fluids that change over time are said to have a memory. Which of the following does not contain synovial fluid.
The synovial membrane is a connective tissue lining the joints and it produces synovial fluid. The surface is permeable to proteins water and small molecules. Low viscosity indicates inflammation.
Normal synovial fluid contains 34 mgml hyaluronan hyaluronic acid 12 a polymer of disaccharides composed of D-glucuronic acid and D-N-acetyl glucosamine joined by alternating beta-14 and beta-13 glycosidic bonds. This paper investigates the practicality of using a small permanent magnet to capture magnetic particles out of high-viscosity biological fluids such as synovial fluid. Examples of shear stresses are squeezing stirring agitat-ing or applying mechanical pressure to the surface of a fluid.
A PMN with inclusions formed by immune complexes. Synovial Membranes. Thus the fluid is usually classified as being non-inflammatory degenerative joint disease or trauma or inflammatory based on the nucleated cell count total protein viscosity types of cells and appearance of cells in the fluid see algorithm.
Synovial fluid is the liquid that surrounds and lubricates joints. Some gels and pastes behave like a fluid when worked or agitated and then settle into a nearly solid state when at rest. In which type of arthritis is the synovial WBC count likely to be greater than 50000microliter.
A structured approach to joint fluid interpretation synovial fluid analysis including some clinical case scenarios to put your knowledge to the test. It is known that patients with OA have diminished HA concentrations in their synovial fluid. Newtonian fluid a fluid in which viscosity is independent of the shear rate eg.
The synovial fluid that coats the knee and elbow joints is a shear-thickening non-Newtonian fluid. But if you bump your knee or elbow the pressure causes the fluid to thicken cushioning and protecting your joints. The association between plasma and follicular fluid folate levels and the pregnancy rate in women enrolled in ICSI cycles Wasan Adnan Abdulhameed Nahlah Abdulmajeed Hasan Ali Ibrahim Rahim A.
But you can agitate. CS also increases the production of hyaluronic acid by synovial cells which subsequently improves the viscosity and the synovial fluid levels. What type of cell is a ragocyte.
In synovial fluid a WBC count of more than 50000 per mm 3 50 10 9 per L and a polymorphonuclear cell count greater than 90 percent have been directly correlated with infectious arthritis. Any of these things can greatly affect the viscosity of a non-Newtonian substance. Blood synovial fluid mucus vitreous humor.
The simulations are used to determine a collection volume with a time. Dynamic or Absolute Viscosity. Normal fluid gives a string longer than 4 cm.
3 Hyaluronic acid HA is a high molecular weight polysaccharide that contributes to the high viscosity of the synovial fluid and had been recognised as the main boundary. When patients have swollen painful joints a synovial fluid analysis can give valuable information about the underlying source of the problem. Numerical simulations are used to predict the trajectory of magnetic particles toward the permanent magnet.
Unfortunately synovial fluid analysis rarely is specific for an underlying cause. The viscosity of SF derives from the polymerisation of hyaluronic acid. A non-newtonian fluid is one in which the viscosity is a function of some mechanical variable like shear stress or time.
Water urine cerebrospinal fluid. Viscosity is estimated by pulling the fluid from the tip of a syringe or pipet. The viscosity of a non-Newtonian fluid can generally be affected by the application of what is called a shear stress.
The synovial fluid is composed mainly of hyaluronic acid glycoproteins and transudate capillaries within the synovial membrane.

Synovial Fluid Viscosity Test Is Promising For The Diagnosis Of Periprosthetic Joint Infection The Journal Of Arthroplasty

Synovial Fluid Wikipedia

A Shear Viscosities Of Human Synovial Fluid In Dependence On The Download Scientific Diagram

Lubricants Free Full Text Development Of A Synthetic Synovial Fluid For Tribological Testing
Synovial Fluid Analysis Physiopedia

The Role Of Lubricin In The Mechanical Behavior Of Synovial Fluid Pnas
What Is Synovial Fluid How Yoga Can Prevent Joint Inflammation
Diagnosis Through Synovial Fluid Analysis
